Robotic Hysterectomy
If your doctor recommends hysterectomy, you may be a candidate for robotic hysterectomy, one of the most effective, least invasive treatment options for a range of uterine conditions. da Vinci Hysterectomy is performed using the da Vinci™ Surgical System, which enables surgeons to perform with unmatched precision and control – using only a few small incisions.
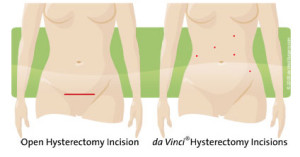
For most patients, robotic hysterectomy can offer numerous potential benefits over traditional approaches to vaginal, laparoscopic or open abdominal hysterectomy, particularly when performing more challenging procedures like radical hysterectomy for gynecologic cancer. Potential benefits include:
- Significantly less pain
- Less blood loss
- Fewer complications
- Less scarring
- A shorter hospital stay
- A faster return to normal daily activities
Moreover, da Vinci provides the surgeon with a superior surgical tool for dissection and removal of lymph nodes during cancer operations, as compared to traditional open or minimally invasive approaches. da Vinci Hysterectomy also allows your surgeon better visualization of anatomy, which is especially critical when working around delicate and confined structures like the bladder. This means that surgeons have a distinct advantage when performing a complex, radical hysterectomy involving adhesions from prior pelvic surgery or non-localized cancer, or an abdominal hysterectomy.
As with any surgery, these benefits cannot be guaranteed, as surgery is both patient- and procedure-specific. While radical hysterectomy or abdominal hysterectomy performed using the da Vinci Surgical System are considered safe and effective, these procedures may not be appropriate for every individual. Always ask your doctor about all treatment options, as well as their risks and benefits.
Other Conditions Treated
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) tumors occurring in at least one quarter of all women. They can grow underneath the uterine lining, inside the uterine wall, or outside the uterus.
Many women don’t feel any symptoms with uterine tumors or fibroids. But for others, these fibroids can cause excessive menstrual bleeding (also called menorrhagia), abnormal periods, uterine bleeding, pain, discomfort, frequent urination and infertility.
Treatments include uterine fibroid embolization – which shrinks the tumor – and surgery. Surgical treatment for uterine tumors most often involves the surgeon removing the entire uterus, via hysterectomy.
While hysterectomy is a proven way to resolve fibroids, it may not be the best surgical treatment for every woman. If, for example, you hope to later become pregnant, you may want to consider alternatives to hysterectomy like myomectomy. Myomectomy is a uterine-preserving procedure performed to remove uterine fibroids.
Treatment
Each year, roughly 65,000 myomectomies are performed in the U.S. The conventional approach to myomectomy is open surgery, through a large abdominal incision. After cutting around and removing each uterine fibroid, the surgeon must carefully repair the uterine wall to minimize potential uterine bleeding, infection and scarring. Proper repair is also critical to reducing the risk of uterine rupture during future pregnancies. Menorrhagia is extensive menstrual bleeding.
While myomectomy is also performed laparoscopically, this approach can be challenging for the surgeon, and may compromise results compared to open surgery. Laparoscopic myomectomies often take longer than open abdominal myomectomies, and up to 28% are converted during surgery to an open abdominal incision.
A new category of minimally invasive myomectomy, robotic myomectomy, combines the best of open and laparoscopic surgery. With the assistance of the da Vinci Surgical System – the latest evolution in robotics technology – surgeons may remove uterine fibroids through small incisions with unmatched precision and control.
Learn More
Please contact our physician referral line at 513-298-DOCS for assistance with identification of a physician who specializes in robotic gynecological/urological procedures.
