First FDA-Approved Treatment for LAM Spearheaded by UC Research
 The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the drug sirolimus for the treatment of lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), a rare lung disorder primarily affecting women. The Multicenter International Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Efficacy and Safety of Sirolimus (MILES) trial, spearheaded by investigators at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, demonstrated that the drug sirolimus (also known as Rapamune® (Pfizer) was shown to be effective in the treatment of LAM. Although not curative, the drug stabilizes lung function and improves functional performance, and has been shown to be generally well-tolerated by patients with LAM.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the drug sirolimus for the treatment of lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), a rare lung disorder primarily affecting women. The Multicenter International Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Efficacy and Safety of Sirolimus (MILES) trial, spearheaded by investigators at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, demonstrated that the drug sirolimus (also known as Rapamune® (Pfizer) was shown to be effective in the treatment of LAM. Although not curative, the drug stabilizes lung function and improves functional performance, and has been shown to be generally well-tolerated by patients with LAM.
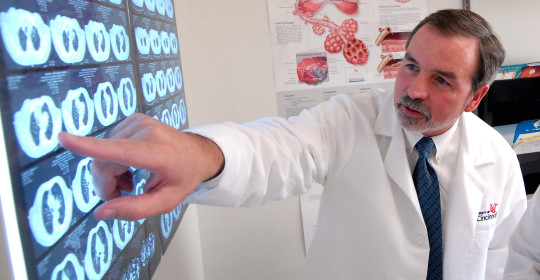
Francis X. McCormack, MD, director of the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine in the UC College of Medicine, was the lead investigator of the MILES trial that enabled the FDA ruling.
“It is very gratifying to see sirolimus join the ranks as one of only a very few approved drugs for diffuse parenchymal lung disease,” McCormack says. “This approval is a testament to the power of patient advocacy and the importance of academic health centers to patients suffering with rare diseases,” says McCormack.

