The UC Esophageal Disease Center is the region’s only team of experts that subspecialize in the treatment of esophageal diseases and esophageal cancer. World-class care is delivered by subspecialists from thoracic surgery, surgical oncology, gastroenterology, medical oncology and radiation oncology as well as a full support team of nurses and ancillary professionals. We promise our expertise in esophageal disorders, delivering hope right here in Cincinnati.
TIF Procedure
(Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication)
The TIF procedure is a minimally invasive method to treat chronic acid reflux, heartburn and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It eliminates the need for abdominal incisions, offering quicker recovery and reduced risks.
Our Capabilities
Our Esophageal Disease experts are a multidisciplinary team focused on providing personalized, comprehensive care. Our collaborative process allows us to provide the right approach for your needs – across both nonsurgical and surgical options.
Compassionate Healing Starts Here
Click below to learn more about where you can find compassionate care.
ABOUT THIS TREATMENT OPTION
Understanding the TIF Procedure
Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) is at the leading-edge of GERD treatment, offering significant relief for the millions suffering from chronic acid reflux. This innovative, less invasive procedure uses the EsophyX device to provide effective treatment without the need for external incisions, setting a new standard in the care of reflux disease. Unlike traditional surgeries that come with longer recovery periods and higher risks, TIF stands out for its minimal downtime and reduced complication rates, making it a preferred choice for eligible patients.
The emergence of the TIF procedure represents a significant shift towards minimally invasive treatments, reflecting the growing demand for procedures that offer both efficacy and a patient-friendly approach. By directly addressing the underlying causes of GERD and improving patients’ quality of life, TIF is not just a medical procedure but a transformation in the management of reflux disease, allowing patients to quickly return to their normal activities with reduced symptoms.
What is the TIF Procedure?
The Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) procedure marks a significant advancement in the minimally invasive treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and chronic acid reflux. Unlike traditional methods such as Nissen fundoplication, which require abdominal incisions and a more extended recovery period, TIF is performed entirely through the mouth. This innovative approach significantly diminishes the procedural risks and recovery time associated with general surgery, offering patients a more appealing alternative.
At its core, the TIF procedure is designed to reconstruct the body's natural anti-reflux barrier. By entering through the mouth, specialists use the EsophyX device to remodel the gastroesophageal valve, enhancing its ability to prevent stomach acid from rising into the esophagus. This procedure effectively addresses the root cause of GERD and reflux symptoms, offering long-term relief without the scars and potential complications of open or laparoscopic surgery.
The TIF procedure's incisionless nature is a breakthrough in reflux treatment, reflecting the broader trend towards less invasive medical interventions. It aligns with patients' desires for treatments that not only resolve their symptoms but also allow for a rapid return to normalcy. For individuals battling with the daily discomforts of acid reflux—such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing—the TIF procedure offers a promising solution that balances efficacy with a patient-friendly approach.
By bridging the gap between pharmacological treatments and traditional surgery, Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication provides a middle ground for patients seeking more substantial relief than medication can offer but are hesitant about undergoing conventional surgery. As such, the TIF procedure represents not just an alternative, but a new standard in the compassionate and effective treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
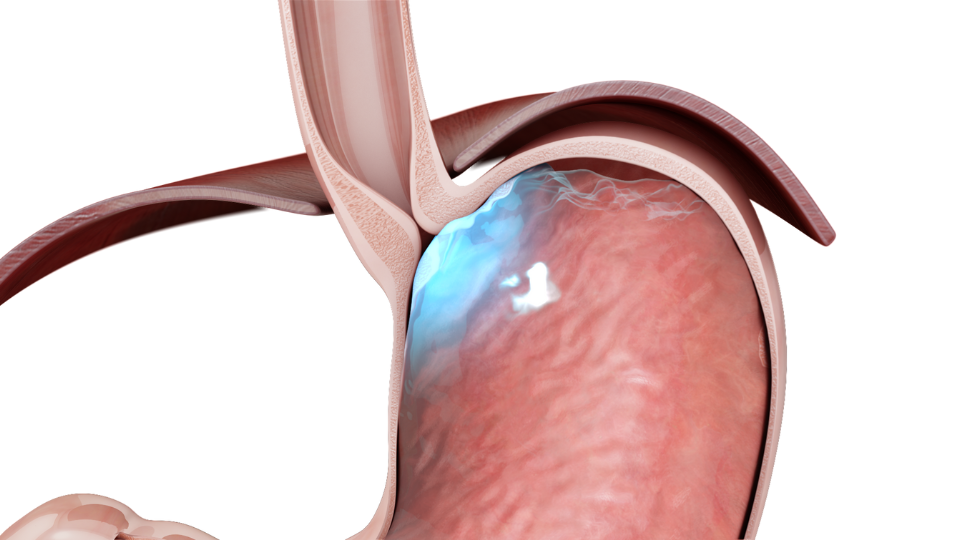
Understanding Acid Reflux and GERD
Acid reflux, occasionally turning into chronic acid reflux or GERD, is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, leading to discomfort and potential damage to the esophageal lining. The underlying cause often relates to a malfunctioning gastroesophageal valve that fails to keep the corrosive stomach acid at bay. GERD symptoms, including heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing, significantly impact patients' quality of life, necessitating effective medical interventions.
Candidates for the TIF Procedure
Identifying the ideal candidates for the Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) procedure is a pivotal step towards ensuring its success and effectiveness. Primarily, this innovative treatment is designed for patients grappling with the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or those diagnosed with a hiatal hernia, who have not found relief through conventional methods such as proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy. The TIF procedure is particularly suited for individuals seeking an alternative to long-term medication or those wishing to avoid the complications and recovery time associated with traditional reflux surgeries.
To determine eligibility for the TIF procedure, healthcare providers conduct a comprehensive assessment, which includes a detailed review of the patient's medical history, symptomatology, and previous treatment responses. This evaluation often involves diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, pH monitoring, and manometry to accurately gauge the severity of the reflux and the structural integrity of the esophagus and gastroesophageal valve. Through this meticulous screening process, medical professionals can identify patients who will most benefit from the procedure, ensuring that the TIF approach is tailored to those with the optimal chance for symptom relief and improved quality of life.
Moreover, candidates for the TIF procedure typically include patients who are:
- Experiencing persistent GERD symptoms despite optimal PPI therapy.
- Suffering from side effects associated with long-term use of acid reflux medication.
- Displaying anatomical issues such as a small hiatal hernia, which contribute to their reflux condition.
- Looking for a less invasive alternative to traditional surgical interventions, with a preference for a quicker recovery period and fewer postoperative restrictions.
For patients fitting these criteria, the TIF procedure offers a compelling treatment option. It not only addresses the physical discomforts associated with acid reflux and GERD, such as chronic heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing, but also provides a path towards reducing dependence on medications and enhancing overall well-being.
The candidacy for the TIF procedure is not a one-size-fits-all determination. Instead, it involves a personalized assessment by a team of medical professionals, including gastroenterologists and surgeons specialized in minimally invasive techniques. By selecting the right candidates, the TIF procedure stands as a testament to the evolution of GERD treatment, embodying a patient-centric approach that prioritizes effective outcomes and quality-of-life improvements.
The Procedure Explained
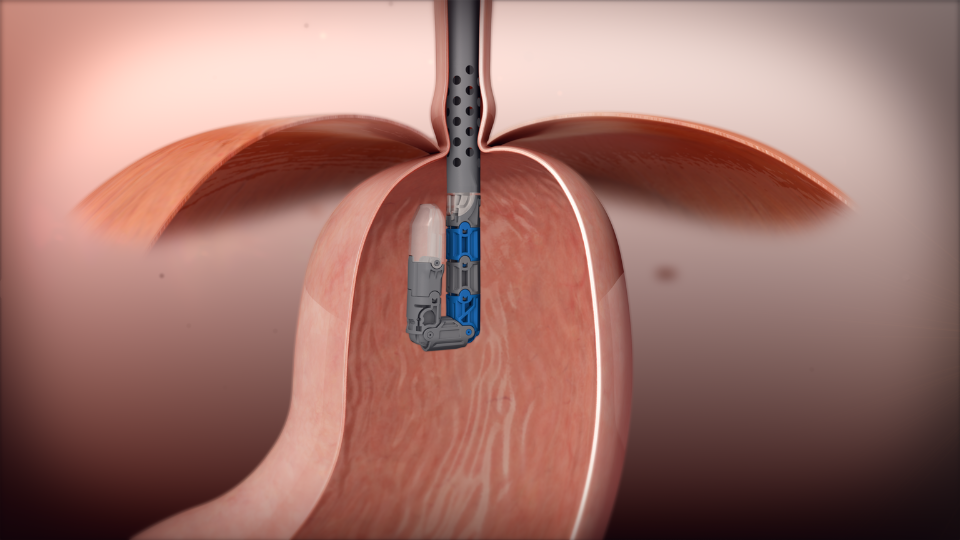
The Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) procedure is a groundbreaking advancement in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgery. Performed under general anesthesia, this innovative technique utilizes the EsophyX device, which is introduced through the patient's mouth, thereby eliminating the need for external incisions.
Step-by-Step Process:

Access and Visualization: The procedure begins with the insertion of the EsophyX device through the mouth, down the esophagus, and into the stomach.
This approach allows for direct visualization of the gastroesophageal junction without any abdominal incisions.
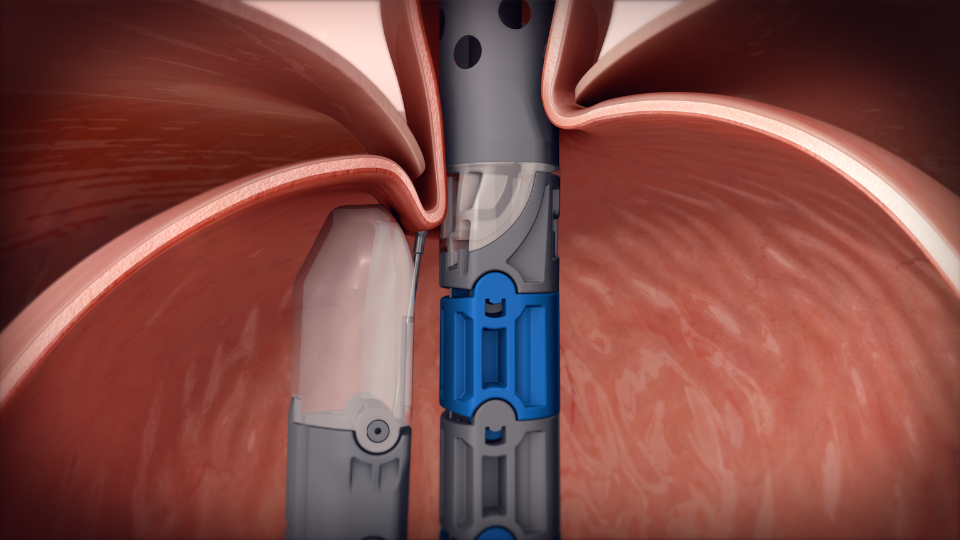
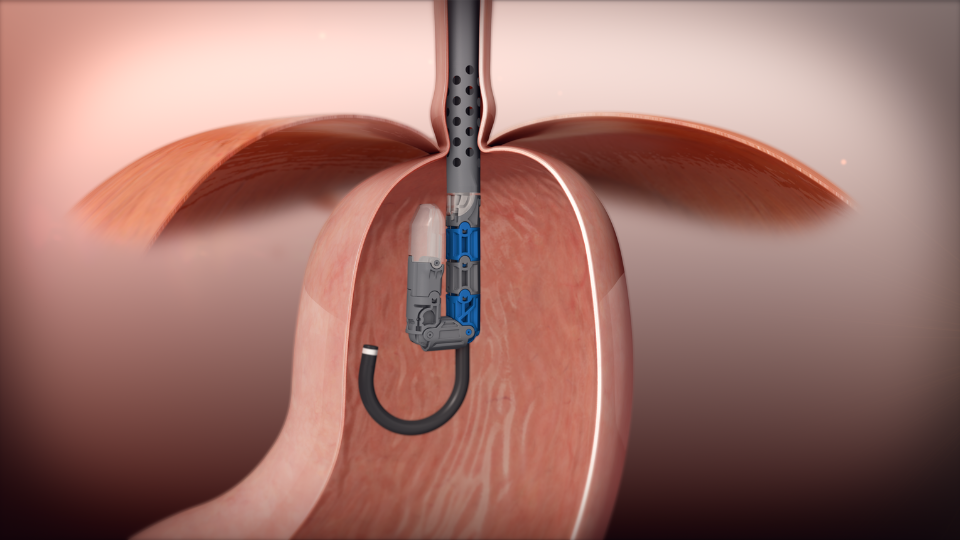
Valve Reconstruction: Once in position, the device is used to create and fasten several folds of tissue at the gastroesophageal junction.
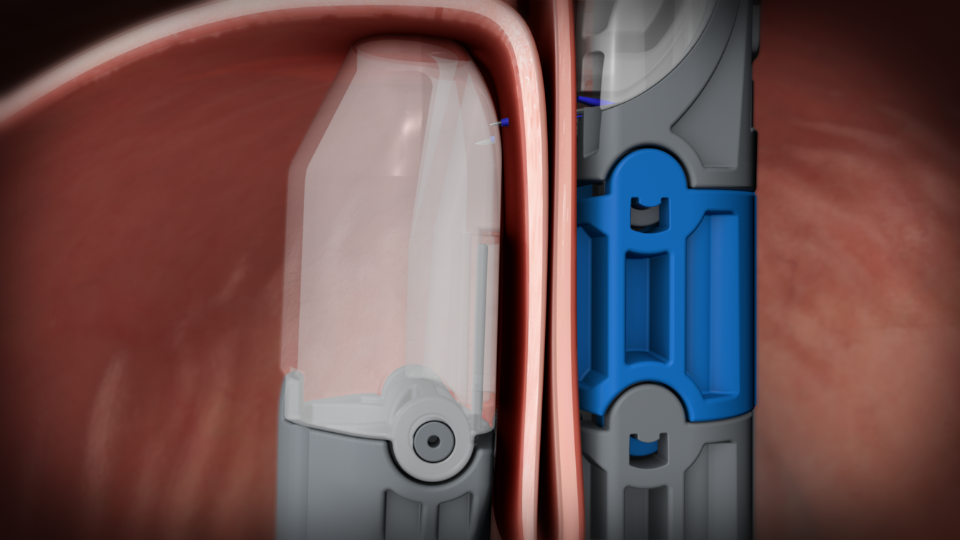
These folds effectively reconstruct the valve between the stomach and esophagus, which is important for preventing acid reflux.
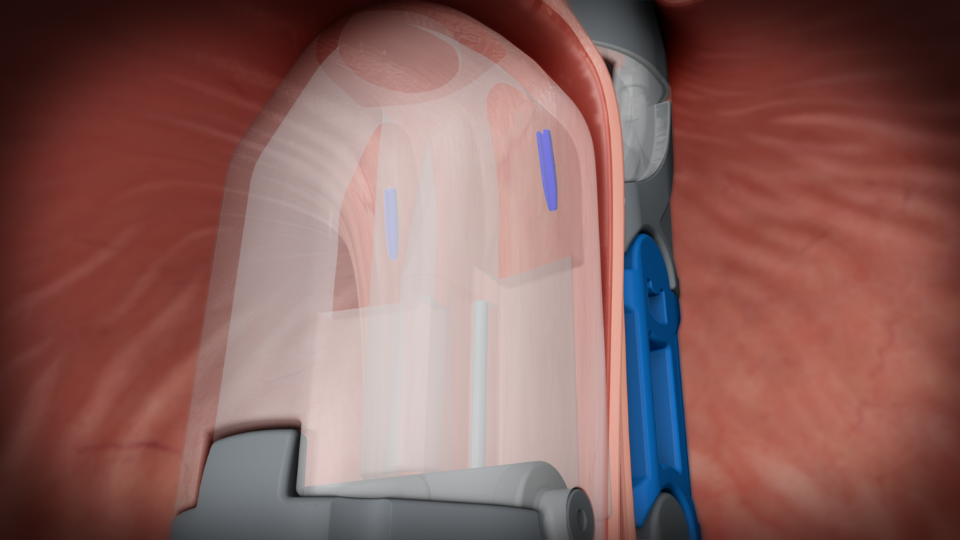
Securing the Valve: The newly created valve is then secured with durable fasteners, ensuring that it remains intact and functional over time.
This step ensures the long-term success of the procedure in mitigating GERD symptoms.
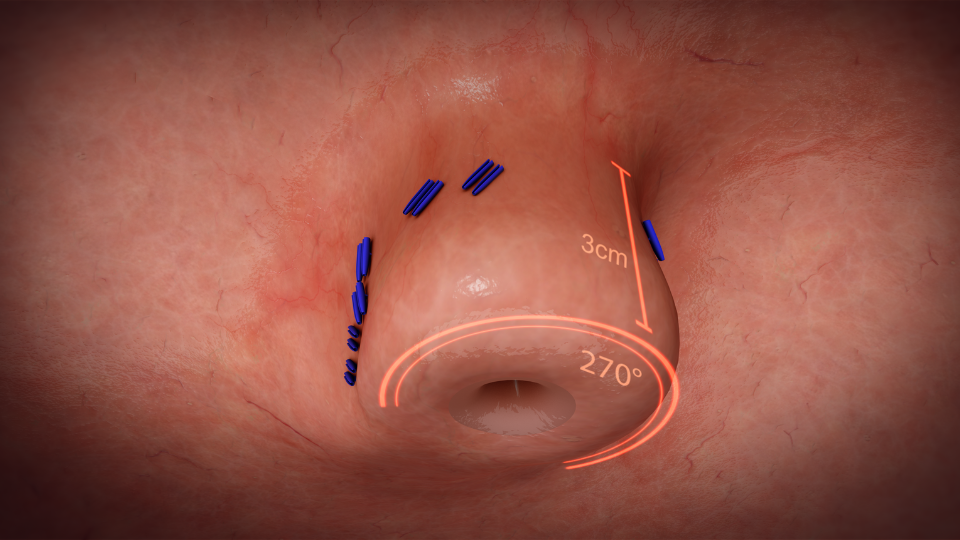
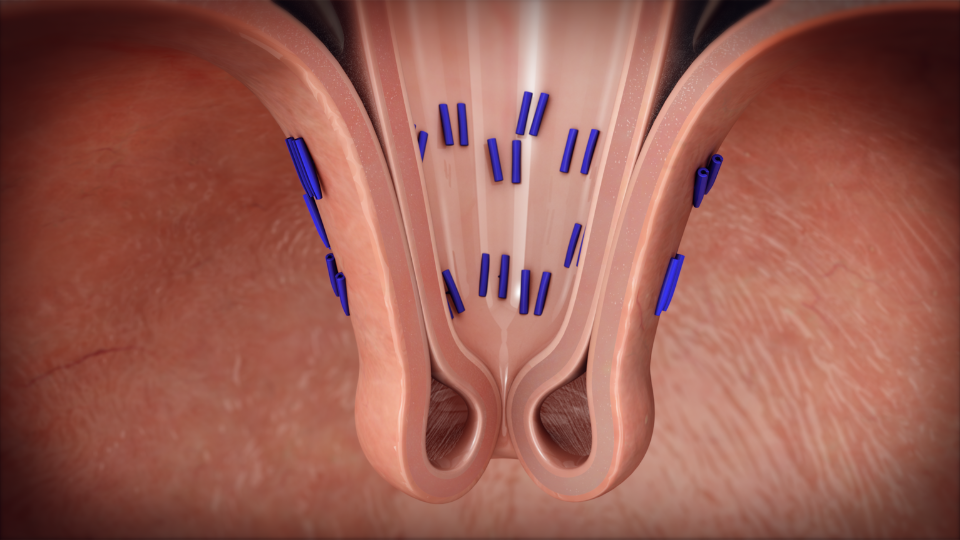
Completion: Upon securing the valve, the EsophyX device is carefully withdrawn, completing the procedure. The entire process typically lasts less than an hour, and most patients are able to return home the same day or after a short observation period.

Advantages Over Traditional Surgery:
The TIF procedure stands out for its incisionless approach, which significantly reduces the risks associated with surgical interventions. Patients benefit from a quicker recovery period, minimal postoperative discomfort, and a lower likelihood of complications such as infection or scarring. Furthermore, the TIF procedure's precision and effectiveness in reconstructing the anti-reflux valve offer durable relief from GERD symptoms, with many patients experiencing a significant improvement in their quality of life.
Postoperative Expectations:
Following the procedure, patients may experience some mild discomfort, such as a sore throat or temporary difficulty swallowing, which typically resolves within a few days. Most individuals can resume their normal diet and activities shortly after, with specific guidelines provided by their healthcare team to ensure optimal healing and effectiveness of the treatment.
In summary, the TIF procedure represents a significant leap forward in the management of acid reflux and GERD. By combining the principles of traditional fundoplication with a less invasive, incisionless technique, this procedure offers patients a safe and effective treatment option, minimizing the impact on their daily lives and maximizing the potential for symptom relief.
Benefits and Risks
The Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) procedure presents a novel approach in the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia, blending the efficacy of traditional surgical methods with the advantages of minimally invasive techniques. Understanding the benefits and potential risks is essential for patients contemplating this procedure.
Benefits:
- Minimally Invasive: One of the most significant benefits of the TIF procedure is its incisionless nature. Unlike conventional surgeries that require cuts in the abdomen, TIF is performed transorally, significantly reducing postoperative pain, the risk of infection, and the length of hospital stay.
- Effective Symptom Relief: Patients undergoing the TIF procedure often experience substantial relief from GERD symptoms, including chronic heartburn, regurgitation, and sleep disturbances caused by acid reflux. This improvement can lead to a decreased need for acid-suppressing medications.
- Quick Recovery: The absence of abdominal incisions allows for a quicker recovery period. Most patients can return to their normal activities within a few days, compared to the weeks typically required after traditional surgery.
- Improved Quality of Life: By effectively addressing the root cause of acid reflux, the TIF procedure can significantly enhance patients' overall quality of life, allowing them to enjoy meals and daily activities without the constant discomfort of GERD.
Risks:
While the TIF procedure is generally considered safe, as with any medical intervention, there are potential risks and side effects that patients should be aware of:
- Temporary Discomfort: Some patients may experience mild to moderate discomfort, such as a sore throat, bloating, or difficulty swallowing in the days following the procedure. These symptoms are usually temporary and resolve on their own.
- Risk of Complications: Although rare, there are potential risks associated with the procedure, including but not limited to, bleeding, infection, or damage to the esophagus or stomach. The risk of such complications is significantly lower than in traditional surgical approaches.
- Need for Additional Treatment: In some cases, patients may require further interventions if the initial procedure does not fully resolve their symptoms or if symptoms recur over time.
Making an Informed Decision:
Choosing to undergo the TIF procedure is a personal decision that should be made after thorough discussion with a healthcare provider. Patients should consider the benefits and risks in the context of their specific medical condition, lifestyle, and treatment goals. Consulting with a specialist in GERD and minimally invasive procedures can provide valuable insights and guidance, ensuring patients make an informed choice about their care.
Aftercare and Recovery
The journey towards recovery and improved quality of life following the Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) procedure is marked by a well-defined aftercare plan. Tailored to promote optimal healing and ensure the long-term success of the treatment, this plan plays a pivotal role in the patient's return to daily activities and relief from GERD symptoms.
Immediate Postoperative Care:
- Dietary Adjustments: Initially, patients are advised to follow a liquid diet, gradually transitioning to soft foods before resuming their regular diet. This phased approach helps the newly formed anti-reflux valve to heal properly and reduces the risk of complications.
- Activity Restrictions: While the recovery period is notably shorter than that of traditional surgeries, patients are encouraged to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few weeks to prevent undue pressure on the treatment area.
Long-Term Recovery and Care:
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the healing process and the effectiveness of the procedure. These visits allow healthcare providers to address any concerns and adjust care plans as needed.
- Managing Expectations: It's important for patients to understand that while many experience significant symptom relief shortly after the procedure, complete recovery and the full benefits of the treatment may take several weeks to manifest.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Considerations: Adopting a healthy diet that avoids trigger foods known to exacerbate acid reflux (e.g., spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol) can complement the benefits of the TIF procedure.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise contributes to the long-term success of the treatment and reduces the risk of GERD recurrence.
Potential Challenges:
- Adjustment Period: Some patients may experience temporary symptoms such as bloating, gas, or difficulty swallowing during the initial recovery phase. These are generally mild and improve with time.
- Ongoing Monitoring: In rare cases, additional interventions may be required if symptoms persist or recur, underscoring the importance of ongoing communication with healthcare providers.
Help Along the Way
Answers to Your Questions about the TIF Procedure
The TIF procedure is a minimally invasive alternative to traditional reflux surgeries like Nissen fundoplication. Unlike traditional surgeries that require abdominal incisions, the TIF procedure is performed transorally (through the mouth), eliminating the need for external incisions.
This approach offers a quicker recovery, with most patients able to return to their normal activities within a few days, and fewer risks associated with the surgical process. In terms of effectiveness, both TIF and Nissen fundoplication are designed to provide long-term relief from GERD symptoms, but the TIF procedure often results in fewer complications and side effects, such as gas bloat syndrome and dysphagia, because it is less invasive and does not involve wrapping the stomach around the esophagus.
The TIF procedure has been shown to be a durable and efficacious treatment option for GERD, with many patients experiencing significant reduction in their symptoms and a decreased need for medication. However, it's important to note that while TIF can significantly improve quality of life and symptom control, a permanent "cure" for GERD is not guaranteed.
Success rates and long-term relief can vary based on individual factors, including adherence to lifestyle changes and the severity of the condition prior to the procedure. Ongoing lifestyle adjustments and follow-up care are crucial for achieving lasting results.
Candidates for the TIF procedure typically include patients with chronic GERD symptoms that are poorly controlled by medication, those experiencing adverse effects from long-term use of acid-suppressing drugs, or patients with a small hiatal hernia (2cm or smaller) that contributes to their reflux.
Patient selection is key to successful outcomes, involving a comprehensive assessment of the patient's medical history, symptom severity, and response to previous treatments. Not everyone is a good candidate for TIF; factors such as large hiatal hernias or severe esophageal motility disorders may necessitate alternative treatments.
After the TIF procedure, patients are advised to follow a phased diet beginning with clear liquids for the first 1-3 days, then progressing to a full liquid diet for the next 2 weeks. Weeks 3-4 introduce a soft texture diet, and weeks 5-6 transition to solid medium texture foods. By week 7, most patients can return to their normal diet. These dietary restrictions are designed to allow the newly reconstructed valve to heal properly and to minimize the risk of complications.
The TIF procedure typically requires less than an hour to complete, with many patients able to leave the hospital the same day or after an overnight stay for observation. Recovery is generally quick, with most patients able to resume non-strenuous activities within a few days. Complete recovery, including the ability to return to all normal activities and lifting restrictions, is usually achieved within 4-6 weeks. The absence of abdominal incisions significantly reduces postoperative discomfort and expedites the healing process.
Yes, the TIF procedure can be revised or repeated if necessary, depending on the patient's situation and the physician's assessment. Long-term outcomes for TIF patients generally include sustained symptom relief and improved quality of life.
By effectively managing GERD, the TIF procedure may also reduce the long-term risks of esophageal damage that could lead to conditions like esophageal cancer, though individual outcomes can vary. Continuous follow-up care is important to monitor and maintain the benefits of the procedure.
After the TIF procedure, patients are recommended to avoid carbonated beverages, acidic drinks, caffeine, and alcohol as part of their recovery diet. Avoiding these foods helps minimize irritation and pressure on the newly formed gastroesophageal valve, promoting proper healing and reducing the risk of complications. Adhering to the prescribed diet phases and avoiding these specific foods contribute significantly to a successful recovery and long-term management of GERD symptoms.
Contact Us
At UC Health, we lead the region in scientific discoveries and embrace a spirit of purpose – offering our patients and their families something beyond everyday healthcare. At UC Health, we offer hope.