Our approach, unique within the region, ensures personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs. We are among the few centers in Ohio certified by the Joint Commission (JCAHO) for performing LVRS, and are commitment to the highest standards of patient care.
Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (BLVR)
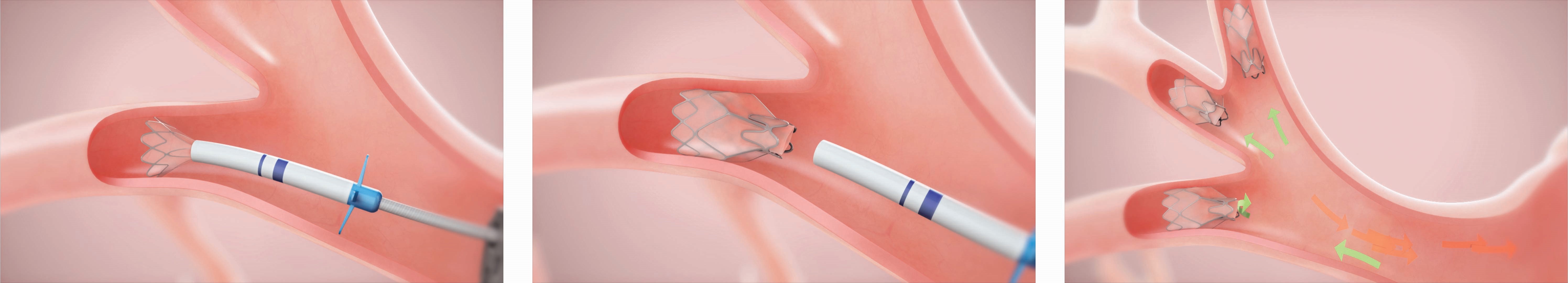
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction is designed to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), particularly in patients with severe emphysema. Blocking airflow to over-inflated areas of the lungs helps healthier lung tissue function better.
Greater Cincinnati’s first BLVR program
As leaders in advanced emphysema treatment, our multidisciplinary team provides individualized care, choosing the best option for each patient. We have led BLVR’s development through clinical trials and remain the region’s most experienced center. Our expertise includes interventions using all available valve types, ensuring optimal treatment.
Compassionate Care Starts Here
Click below to learn more about lung volume reduction therapies.
ABOUT THIS TREATMENT OPTION
Understanding Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) is an innovative procedure designed to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), particularly in patients with severe emphysema. This minimally invasive technique aims to reduce lung volume by targeting hyperinflated areas of the lungs, allowing healthier lung tissue to function more effectively.
As the prevalence of COPD continues to rise, the need for effective treatment options becomes increasingly important. BLVR offers hope for patients struggling with debilitating symptoms, improving their quality of life and overall lung function.
Understanding Lung Volume and Its Importance
Lung volume refers to the amount of air the lungs can hold, which is essential for effective lung function. It plays a critical role in the respiratory process, allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to be exchanged.
Key Components of Lung Volume
- Tidal Volume: The amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing.
- Vital Capacity: The maximum amount of air a person can exhale after a maximum inhalation.
- Residual Volume: The air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation.
Impact on Patients with Chronic Lung Diseases
For patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other lung conditions, maintaining optimal lung volume used for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide (also known as tidal volume) is vital. Reduced tidal volume with excessive trapped air (residual volume) can lead to:
- Decreased Oxygen Exchange: Insufficient air can hinder the lungs' ability to oxygenate the blood effectively. Patients may require chronic oxygen with exertion due to this.
- Increased Work of Breathing: Patients may experience more effort to breathe, leading to fatigue and discomfort.
- Worsening Symptoms: Conditions like emphysema can cause hyperinflation, trapping air and further reducing functional lung capacity. Trapped air can also cause airways to narrow from external compression leading to worsening chronic cough – both productive and non-productive.
Importance of Healthy Lung Function
Healthy lung function is crucial for overall well-being. It supports:
- Physical Activity: Adequate lung volume allows for better endurance and participation in daily activities.
- Quality of Life: Improved lung function can enhance daily living and reduce the burden of respiratory symptoms.
Understanding lung volume and its implications can empower patients to engage in preventive measures and seek appropriate treatments, ensuring better management of their respiratory health.
The Need for Lung Volume Reduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), particularly severe emphysema, leads to significant lung hyperinflation. This condition occurs when air becomes trapped in the lungs, preventing complete exhalation and resulting in reduced lung function.
Impact of Hyperinflation
- Breathing Difficulties: Patients often experience shortness of breath, especially during physical activities.
- Decreased Quality of Life: The inability to breathe comfortably can limit daily activities and overall well-being.
- Increased Work of Breathing: Hyperinflation forces the respiratory muscles to work harder, leading to fatigue and further respiratory distress.
Role of Lung Volume Reduction
Lung volume reduction is a therapeutic approach aimed at alleviating these symptoms. By removing or, reducing or blocking the volume of damaged lung tissue, patients can experience:
- Improved Breathing: Reducing hyperinflation allows for better airflow and easier breathing.
- Enhanced Exercise Capacity: Patients often find they can engage in physical activities with less effort and discomfort. Patients may be able to come off oxygen depending on individual circumstances.
- Better Quality of Life: Alleviating symptoms can lead to increased participation in daily activities and improved emotional well-being.
This procedure is particularly beneficial for patients with severe COPD with emphysema, as it targets the damaged areas of the lungs, allowing healthier lung tissue to function more effectively. By addressing the issues caused by trapped air and hyperinflation, lung volume reduction can significantly improve the overall health and quality of life for these patients.
Overview of Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (BLVR)
Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (BLVR) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to improve lung function in patients with severe emphysema, a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This innovative technique utilizes a bronchoscope—a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and tools—to access the lungs without the need for large incisions.
The Procedure
- Accessing the Lungs: The procedure begins with the insertion of the bronchoscope through the mouth and into the airways. This allows the physician to visualize the lungs and assess the extent of damage.
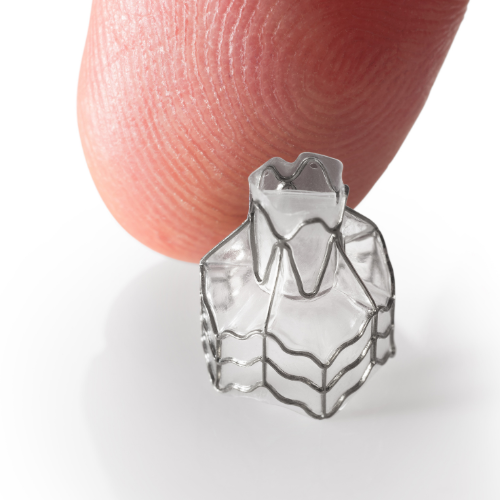
- Endobronchial Valves: During BLVR, small devices called endobronchial valves are placed in specific airways. These valves are designed to block airflow to the over-inflated areas of the lungs, allowing healthier parts to expand and function more effectively. UC Health utilizes both one-way valves on the market: Pulmonx Zephyr valves and Olympus Spiration valves, personalizing selection and treatment for the individual.

Role of Interventional Pulmonologists
Interventional pulmonologists are specialists trained to perform BLVR. They play a crucial role in:
- Patient Evaluation: Assessing whether a patient is a suitable candidate for the procedure based on their lung function, individual anatomy, and overall health.
- Procedure Execution: Skillfully performing the bronchoscopic placement of valves, ensuring optimal outcomes. UC was part of the initial trials for bronchoscopic lung volume reduction through the EMPROVE trial.
- Post-Procedure Care: Monitoring patients after the procedure in the hospital for at least three nights to monitor for any potential complications and support recovery.
BLVR offers a promising option for patients seeking relief from the debilitating symptoms of severe emphysema, enhancing their quality of life through improved lung function.
Benefits of Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) offers several advantages over traditional surgical methods, making it an appealing option for patients with severe emphysema.
Minimally Invasive Approach
- Less Invasive: BLVR is a minimally invasive procedure, which means it requires no large incisions. This results in reduced inflammation and to the body.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients typically spend less time in the hospital compared to those undergoing traditional lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) – on average for 3 nights spent in the hospital.
- Reversible: If for whatever reason a patient does not find benefits from valve placement, valves can be removed with minimal longstanding consequences.
Quicker Recovery Time
- Faster Return to Daily Activities: Many patients experience a quicker recovery, allowing them to return to their daily routines sooner.
- Reduced Pain: The minimally invasive nature of the procedure often leads to less postoperative pain (often painless), enhancing patient comfort.
Fewer Complications
- Lower Risk of Complications: BLVR generally has a lower risk of complications such as infection or prolonged recovery compared to LVRS.
- Targeted Treatment: The use of endobronchial valves allows for targeted treatment of hyperinflated areas of the lungs, minimizing damage to healthy lung tissue.
Enhanced Quality of Life
- Improved Lung Function: Patients often report improved lung function and reduced symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
- Mortality Benefit: There are supportive studies that describe a survival benefit with BLVR.
- Improved Wellness: Patients often report improved wellness scores for depression and anxiety stemming from their breathing after BLVR.
- Supportive Care: Post-procedure, patients can engage in pulmonary rehabilitation with increased ambulation distances and endurance, which is crucial for maximizing recovery and improving overall health.
Overall, BLVR presents a promising option for patients seeking relief from the debilitating effects of severe emphysema, combining effectiveness with a more comfortable recovery experience.
Risks and Considerations
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) is generally safe, but like any medical procedure, it carries potential risks. Understanding these risks can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Common Risks
- Pneumothorax: This is a condition where air leaks into the space between the lung and chest wall, potentially causing lung collapse. While it can occur during the procedure, it is usually manageable with prompt medical attention and the reason that patients are admitted for 3 nights post-procedure.
- Respiratory Infections: Patients may be at increased risk for infections following BLVR due to changes in lung function and the introduction of a foreign material to the lungs (the endobronchial valves themselves).
Other Considerations
- Valve Migration: In rare cases, the endobronchial valves may shift from their intended position due to inflammation surrounding the valves, which can affect their effectiveness and may require additional procedures to correct. It is incredibly rare to cough up a valve however. Additional bronchoscopic procedures may be necessary to replace migrating valves.
- Patient Selection: Not all patients are suitable candidates for BLVR. A thorough pre-procedure evaluation is essential to assess lung function, overall health, and specific lung conditions. This evaluation helps ensure that the procedure's benefits outweigh the risks. Some patients may be better suited to proceed with lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS), and this assessment occurs concurrently.
By discussing these risks and considerations with healthcare providers, patients can better understand what to expect and how to prepare for the procedure.
Who is a Candidate for BLVR?
Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) is particularly beneficial for patients suffering from severe emphysema, a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Identifying suitable candidates is essential for maximizing the procedure's effectiveness.
Key Characteristics of Candidates
- Severity of Emphysema: Candidates typically have severe emphysema, which significantly impairs lung function and quality of life. The location of emphysema does not necessarily impact candidacy. BLVR can be performed on heterogenous emphysema (either occurring worse in the upper or lower lung fields) or homogenous emphysema (occurring equally throughout the lungs). Alpha-1 antitrypsin disease (a genetic disorder contributing to COPD and emphysema production) can also be treated with BLVR.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: These tests assess lung function and help determine if a patient is a suitable candidate. Key metrics (ideally using body plethysmography rather than nitrogen washout) include:
- Forced expiratory volume (FEV1)
- Total lung capacity (TLC)
- Residual volume (RV)
Additional Considerations
- Overall Health: Candidates should be in stable health, with well-controlled comorbidities that could complicate the procedure or recovery.
- Previous Treatments: Patients who have ongoing shortness of breath and reduced endurance who have not responded well to other treatments, such as medications or pulmonary rehabilitation, may be considered for BLVR.
By carefully evaluating these factors, healthcare providers can identify patients who are most likely to benefit from bronchoscopic lung volume reduction, ultimately improving their lung function and quality of life.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After undergoing bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR), patients can expect a structured recovery process that is vital for optimal outcomes.
Initial Recovery
- Hospital Stay: Most patients will remain in the hospital for a short period (3 nights) for monitoring. This allows healthcare providers to assess lung function and manage any immediate post-procedure complications. Patients are at the highest risk of complications during this time, and we can assure patient safety.
- Vital Signs Monitoring: Regular checks on oxygen levels and respiratory function are essential to ensure stability.
Follow-Up Care
- Scheduled Appointments: Follow-up visits with healthcare providers are crucial to evaluate recovery progress and lung function improvements. Our dedicated BLVR nurse coordinator will provide a phone call at 1 and 2 weeks post-procedure, and then patients are seen at 3, 6, and 12 months after the intervention.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Engaging in a pulmonary rehabilitation program is highly recommended. This program focuses on
- Exercise Training: Tailored exercises to enhance lung capacity and overall endurance.
- Education: Learning about managing lung health and recognizing symptoms that may require medical attention.
Long-Term Health
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients are encouraged to adopt healthier habits, such as quitting smoking and vaping, as well as maintaining a balanced diet, to support lung health.
- Monitoring Lung Function: Regular assessments of lung function will help track improvements and adjust rehabilitation strategies as needed.
By prioritizing post-procedure care and participating in pulmonary rehabilitation, patients can significantly enhance their recovery, regain lung function, and improve their overall quality of life.
Why UC Health
Expertise in Advanced Emphysema Care
Regional Leaders in BLVR
We pioneered bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) and remains the most experienced center in Greater Cincinnati. Our experts have participated in the initial clinical trials, ensuring top-level care for advanced emphysema patients.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Our advanced emphysema program offers a personalized, multidisciplinary approach to each patient. We work closely with specialists across various fields to determine the best treatment option, focusing on individualized care that meets each patient’s unique needs.
Access to Leading Technologies
We provide intervention using both valve types available on the market, ensuring that we select the optimal solution for every patient. Our team utilizes the latest innovations and technologies, offering cutting-edge care in emphysema treatment.
Contact Us
At UC Health, we lead the region in scientific discoveries and embrace a spirit of purpose – offering our patients and their families something beyond everyday healthcare. At UC Health, we offer hope.